pearCast - A Peer-to-Peer Audio Broadcasting App
pearCast is a decentralized, peer-to-peer (P2P) audio broadcasting application that enables users to broadcast and listen to live audio streams directly from a desktop app without relying on centralized servers or third-party STUN/TURN servers. Using Hyperswarm for P2P networking and WebRTC for audio streaming, pearCast allows users to create and join audio broadcast stations effortlessly.
Run the app on pear!
pear run pear://q3rutpfbtdsr7ikdpntpojcxy5u356qfczzgqomxqk3jdxn6ao8y
Key Features
- Create or Join a Station: Host a broadcast or tune into an existing one.
- Microphone Selection: Broadcasters can select and switch between available audio input devices.
- Real-time Audio Streaming: Capture and stream live audio to all connected listeners using WebRTC.
- Decentralized Networking: Peer-to-peer connections using Hyperswarm, eliminating the need for centralized servers or third-party STUN/TURN servers.
- Broadcaster-Hosted TURN Functionality: The broadcaster hosts their own TURN-like functionality over Hyperswarm, enabling direct connections.
- Error Handling: Logs peer disconnections and connection resets without crashing.
Technologies Used
- Hyperswarm: For discovering and connecting peers based on a shared "topic" key, ensuring direct connections without the need for central servers.
- WebRTC: For real-time audio streaming between peers, with custom signaling over Hyperswarm.
- Web Audio API: A powerful API for capturing and processing live audio in the browser.
- Bootstrap: For responsive and user-friendly UI elements.
- JavaScript & Node.js: Application logic, error handling, and P2P networking.
- Pear CLI: Pear CLI.
Table of Contents
Getting Started
Prerequisites
- Node.js: Required to install dependencies and run the app.
- Pear CLI: Use the Pear CLI
Installation
-
Clone the Repository:
git clone https://git.ssh.surf/snxraven/pearCast.git cd pearCast -
Install Dependencies:
npm install -
Run the App:
pear run --dev .
Note
: If you’re not using the Pear CLI, you can serve
index.htmlthrough a local web server (e.g., using theLive Serverextension in VSCode or a simple HTTP server).
User Guide
Creating a Broadcast Station
- Click "Create Station": Initiates a new station and begins capturing audio from the microphone.
- View Station ID: Once created, the station will display a unique ID (based on a cryptographic key), which can be shared with others to join.
- Audio Input Selection: Choose the desired microphone input from a dropdown menu, then click "Apply" to switch.
- Leaving the Broadcast: Click "Leave Broadcast" to end the session, which will also disconnect all connected peers.
Joining a Broadcast Station
- Click "Join Station": Opens a modal window.
- Enter Station ID: Input the ID shared by the broadcaster and click "Join" to connect.
- Listen to Broadcast: Audio from the broadcast will begin streaming in real-time using WebRTC.
- Leaving the Broadcast: The listener can leave the broadcast by clicking "Leave Broadcast" or closing the connection in the browser.
Changing Audio Input
For Broadcasters Only: Broadcasters can change their microphone input while streaming. Simply select a different device in the "Audio Input Source" dropdown and click "Apply" to switch. The broadcast will automatically start using the newly selected device.
Technical Details
How P2P Connections are Handled
The core networking functionality uses Hyperswarm. Each station (both broadcaster and listener) connects to a unique "topic" based on a cryptographic key. Hyperswarm manages discovery and connection setup without central servers by joining a Distributed Hash Table (DHT). Key components include:
-
Generating a Station ID: When a station is created,
crypto.randomBytes(32)generates a 32-byte cryptographic key that uniquely identifies the broadcast. Hyperswarm joins this topic in "server mode" for the broadcaster and "client mode" for listeners. -
Peer Connections: Both broadcaster and listener connections are managed by Hyperswarm's
swarm.on('connection')event, which establishes a direct connection for signaling and data transfer. -
Custom Signaling: The application uses custom signaling over Hyperswarm connections to exchange WebRTC session descriptions (SDP) and ICE candidates.
Custom Signaling over Hyperswarm
- Data Channels for Signaling: Hyperswarm connections (
conn) are used as data channels for exchanging signaling messages between the broadcaster and listeners. - Signaling Messages: Offers, answers, and ICE candidates are serialized into JSON and sent over Hyperswarm connections.
- PeerConnection Configuration: WebRTC
RTCPeerConnectionis configured with an emptyiceServersarray, relying on the Hyperswarm network for connectivity.
Broadcaster-Hosted TURN-like Functionality
- Broadcaster as Relay: The broadcaster effectively acts as a relay for media streams, mimicking TURN server behavior within the Hyperswarm network.
- No Third-Party Servers: This approach eliminates the need for external STUN/TURN servers, as the broadcaster handles the necessary signaling and relaying over Hyperswarm.
- NAT Traversal: Hyperswarm assists in establishing connections between peers even when they are behind NATs.
Audio Capture and Streaming
Using WebRTC and the Web Audio API, pearCast captures and streams audio from the broadcaster to listeners.
- Audio Context Setup: When a station is created, an
AudioContextis initialized for audio processing. - Local Media Stream: The broadcaster captures audio using
navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia()and adds the tracks to theRTCPeerConnection. - Real-time Audio Streaming: WebRTC handles the streaming of audio data between the broadcaster and listeners.
- Playback for Listeners: Listeners receive the audio stream via the
ontrackevent and play it using an<audio>element.
Error Handling and Disconnection Logging
- Graceful Peer Disconnects: Each connection includes error handling and disconnect logging. A connection reset (e.g.,
ECONNRESET) or manual disconnect is logged without crashing the app. - ICE Candidate Handling: The application properly handles ICE candidates exchanged over Hyperswarm, ensuring a stable connection even in the absence of external servers.
Code Structure
HTML (index.html)
index.html contains the core layout and UI components:
- Station Controls: Create or join a station and leave the broadcast.
- Audio Input Selection: Available to broadcasters only, allowing them to change input sources.
- Bootstrap Modals: Provides a user-friendly modal interface for creating and joining stations.
JavaScript (app.js)
app.js contains the main application logic:
- Station Management: Functions to create or join stations, handle connections, and manage disconnects.
- Peer Connections: Manages WebRTC
RTCPeerConnectioninstances for each peer. - Custom Signaling: Implements signaling over Hyperswarm connections for exchanging offers, answers, and ICE candidates.
- Audio Capture & Streaming: Configures audio context, captures microphone data, and handles streaming via WebRTC.
- Error Handling: Includes connection reset handling and graceful disconnect logging.
- Audio Source Selection: Enables broadcasters to choose from available audio input devices.
Example Screenshots
| Feature | Screenshot |
|---|---|
| Create Station | 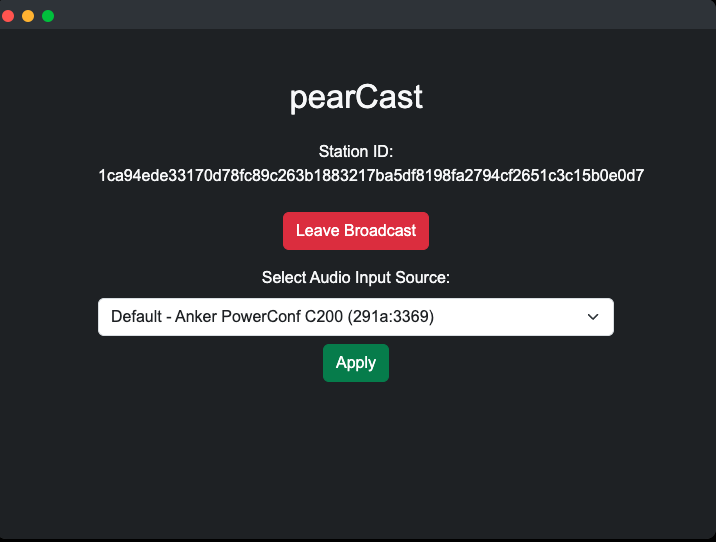 |
| Join Station Modal | 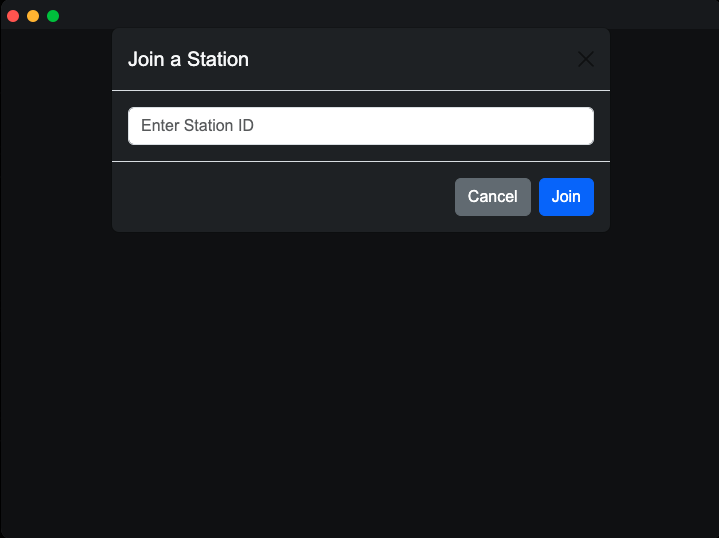 |
| Audio Input Control | 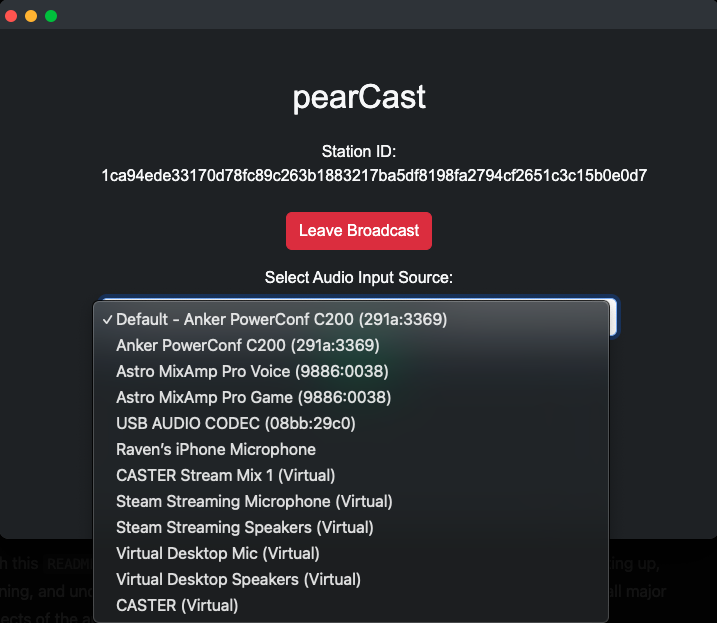 |
Troubleshooting
-
Connection Issues:
- Ensure both broadcaster and listener have network connectivity.
- Check that the Station ID is correctly entered.
-
No Audio Device Detected:
- Ensure your browser has permission to access the microphone, and refresh the device list if necessary.
-
Audio Source Changes Not Applying:
- If changing the audio input source doesn't take effect, ensure you click "Apply" after selecting the device.
-
NAT Traversal Issues:
- While Hyperswarm assists with NAT traversal, some restrictive network environments may still cause connectivity problems.